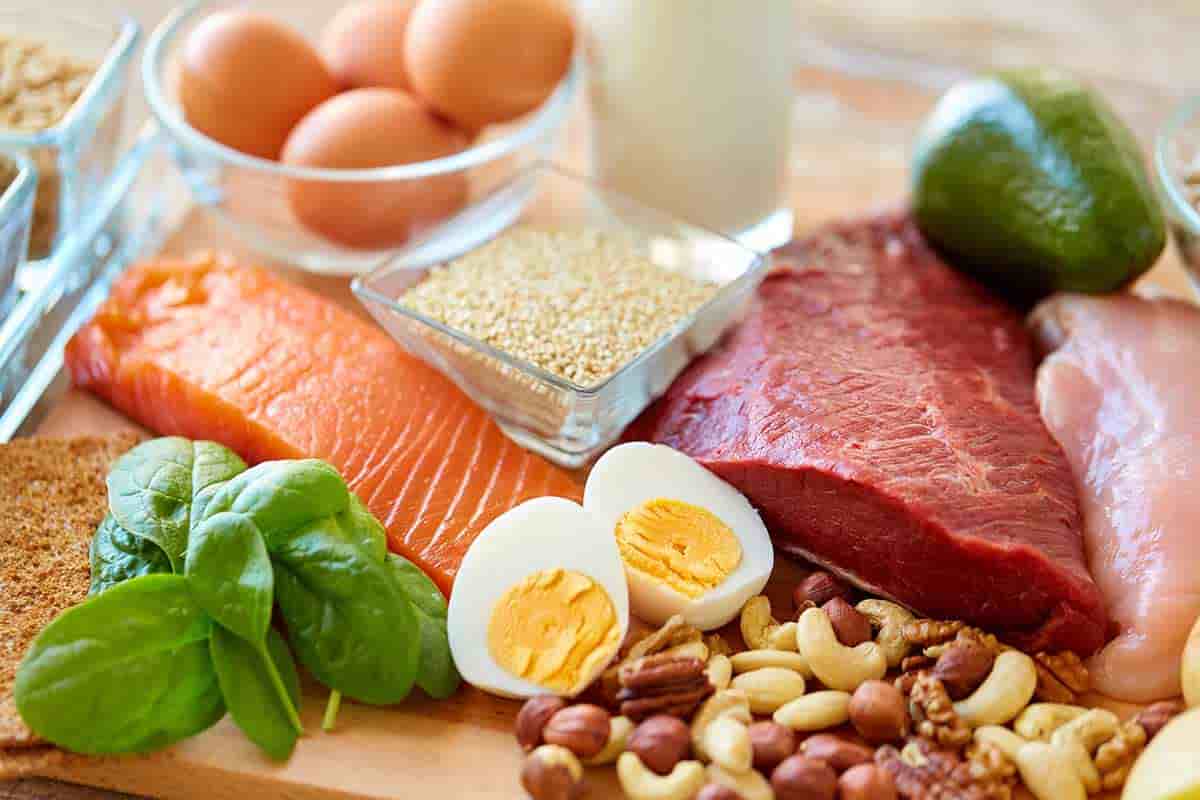
Nutrients are compounds that the body needs in large quantities. Carbohydrates (found in foods like bread and pasta) and fats (from oils or butter), along with other vitamins and minerals are some common types of nutrients that our bodies need regularly.
The seven most common types of nutrients are:
- Proteins
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin B12
- Calcium
- Vitamin D
Read on to discover the seven most common types of nutrients and why our bodies need them. Additionally, we will discuss some examples of nutrient-rich foods that we should be including in our diets.
Article Contents
What Are Nutrients?
Nutrients are substances that provide nourishment to living organisms. Nutrient-dense foods contain a high level of nutrients at low levels of calories, making them great for weight management and overall good health.
Nutrients are compounds that provide energy to the body. Nutrients make hair thicker and skin smoother and give your immune system a boost. In addition, some nutrients keep muscles healthy and aid you in some forms of physical activity.
Nutrients also come from vitamins such as Vitamin D, which regulates calcium absorption into bone tissue.
What Does Our Body Do with Nutrients?
Our bodies require nutrients for several vital functions that help us stay healthy and active. Nutrients provide energy so that we can stay active during physical activity. For example, vitamin B is used as a fuel source for muscle contractions, which also helps users make sure muscles are healthy enough to contract properly if needed.
Our bodies use nutrients to keep them healthy. Bodies process nutrients through digestion and absorption. When nutrients are digested, they enter the bloodstream, where they’re absorbed into cells to be used for energy production or stored in tissues such as muscle tissue and fat cells.
Our bodies need nutrients to:
- Nourish cells, tissues, and organs to keep us healthy.
- Protect our bodies against disease by strengthening immunity.
- Regulate blood sugar levels after eating.
- Produce red blood cells, hormones, and neurotransmitters
- Maintain a healthy weight
Nutrients also provide us with energy for our muscles to contract correctly. This is especially important when we need muscle strength during physical activities or strenuous exercise such as lifting weights or playing sports.
What Are the 7 Most Common Types of Nutrients?

What Are Proteins?
Proteins are common nutrients that are needed by the body. Proteins can come from animal or plant sources—or both!
Proteins are the building blocks of muscle tissue, and they are the primary source of energy for our muscles. They perform many essential functions in the body, especially when you need muscle strength during physical activities or strenuous exercise.
Sources common in Western diets include:
- Meat (beef)
- Dairy products such as cheese or yogurt
- Eggs
- Seafood like shrimp and crab
- Soy products such as tofu and tempeh
Legumes offer a good balance of protein compared to other foods. Protein supplements are also available for those that don’t eat many of the above sources or need additional protein in their diet.
What Are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates come from plant foods like vegetables and grains. They also include sugars found naturally on fruits or refined table sugar and honey, syrups, and sweeteners (i.e., sucrose). Legumes such as peas/beans offer a good balance of carbohydrates compared to other common foods, primarily containing fats/oils or proteins only.
Carbohydrates are common nutrients that come from plant foods like vegetables and grains. They also include sugars found naturally on fruits or refined table sugar and honey. Legumes such as peas/beans offer a good balance of carbohydrates compared to other common foods.
A healthy diet will provide 55-60% carbohydrates – the key is choosing whole grain versions with added fiber rather than white flour products, high in sugar but low in other essential nutrients.
Carbohydrates are common nutrients that come from plant food sources like vegetables and grains. Carbohydrates can be classified by glycemic index:
- Fast release (e.g., white bread).
- Slow-release (whole-wheat bread).
They can be found in sugar, fruits, and vegetables like carrots. Fast-release carbs should not make up more than 45% of your diet because they don’t provide long-term energy for the body but give you fast-acting fuel to work out harder or longer.
Slow-release carbohydrates are the opposite. They take longer to digest, so you can go for a long time before feeling hungry or needing another meal.
How Do Fats Help Our Bodies?
Fat is needed to produce certain hormones such as estrogen; it also helps regulate mood by supplying energy when a person feels tired or stressed.
Fats help our bodies by serving as fuel and transporting nutrients throughout our body for use in various functions. This includes maintenance and repair of cells.
The common types of fats are:
- Saturated: Saturated fats come from animal sources like meat, eggs, and dairy products.
- Unsaturated: Unsaturated fats come from vegetable oils as well as nuts and seeds.
- Trans fat: Trans fat comes in solid form but has a liquid counterpart, usually used in processed foods.
Fats are an essential nutrient because they provide energy in calories and help you stay full longer. The body stores excess fat by producing lipids (fats) from carbohydrates or other nutrients it has consumed that were not used immediately as fuel.
Why Do Our Bodies Need Vitamin C?
Vitamin C is common in many fruits and vegetables. Vitamin C also acts as an antioxidant, helping your cells resist damage from free radicals, which are common byproducts of metabolism and exposure to environmental toxins.
Our bodies require vitamin C to form collagen, which is an essential component of tissue and bone. Vitamin C plays a crucial role in forming skin cells by ensuring that they stick together to create healthy skin.
Vegetables high in Vitamin C include:
- Broccoli
- Cabbage
- Kale
- Brussels sprouts
Fruits high in vitamin C include:
- Citrus fruits such as oranges or grapefruits.
- Strawberries
- Pineapple
- Guava
Each orange contains about 100 mg of Vitamin C (more if you eat the peel). If intake exceeds 2000mg per day, side effects such as diarrhea can occur but usually disappear when the person cuts back on their dose or takes a break from taking supplements altogether. Some people get too little in their diet because they avoid fruits and vegetables with high acidity levels or drink alcohol since it also inhibits the absorption of Vitamin C.
Why Do Our Bodies Need Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 is common in animal-based foods like poultry and seafood. Some plant-based choices include beans and soy milk, but Vitamin B12 is found at lower levels in plant-based options and must be eaten more often to meet the RDA of two milligrams per day.
Our bodies require Vitamin B12 to help keep our nerves and blood cells healthy and maintain the health of DNA. Vitamin B12 also helps to break down fats and proteins for use as energy.
In a common condition called pernicious anemia, caused by low vitamin B12 in the body, red blood cells are often large or wide because they have not been able to divide properly due to a lack of Vitamin B12.
A person with this type can feel very tired after eating even though their stomach feels full–and may lose weight since appetite is decreased.
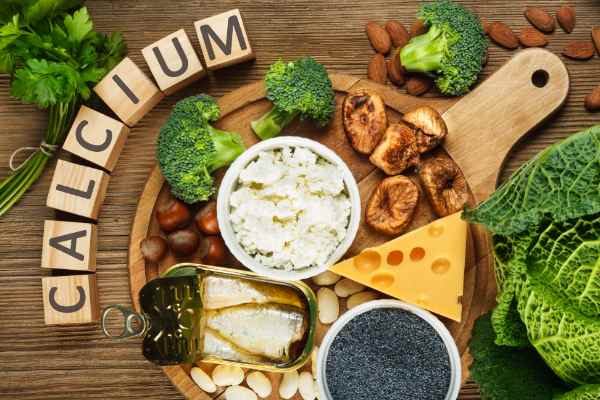
What is Calcium?
Calcium is a common nutrient that’s found in many foods. It’s needed for strong bones and teeth and normal brain function. Calcium is also vital to the release of energy from food and activation of some nerve impulses and other essential functions.
Calcium is a common mineral that is found in a variety of foods. For example, dairy products such as milk and yogurt are excellent sources. Metabolism increases when one has higher levels of calcium intake since this nutrient contributes to energy production.
To consume enough calcium through the diet or supplements, adults need 1000-1200 mg of calcium per day.
The best sources of calcium are dairy products such as:
- Milk
- Cheese
- Yogurt
- Dark green vegetables
- Broccoli
- Almonds
- Soybeans and more.
Calcium supplements are also common for people who have trouble getting enough calcium in their diets. Over-the-counter pills come with 1000 mg of calcium per tablet. However, it is recommended that adults only take 500 mg since excessive calcium intake can harm the kidneys.

How Does Vitamin D Help Our Bodies?
Get enough Vitamin D by eating foods rich in it or spending some time outdoors without sunscreen. If your doctor says that you need more than what you’re getting, then ask them about supplements. But make sure not to get too much of a good thing – any extra will go into fat storage instead of being put towards other critical bodily functions.
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, so it’s essential to get enough vitamin D from food or sun exposure (depending on how much you’re outside). If there isn’t enough vitamin D, then your body will take what it needs out of your bones, leading to problems like osteoporosis.
Vitamin D is common in foods like:
- Eggs
- Milk
- Salmon
- Vitamin D intake can also come from sun exposure.
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient because it helps the body absorb and utilize calcium. It also prevents heart disease and supports immune function.
While our bodies produce vitamin D when we’re in contact with sunlight, long-term lack of sun exposure can lead to low levels of this critical nutrient. Experts recommend people get at least 600 IU of vitamin D each day.
3 Examples of Nutrient-Rich Foods
Some of the best nutrient-rich foods are dark green vegetables. These are common foods that help your body get all the nutrients your body needs to stay healthy. They’re also a great way to start eating more vegetables in general!
Some Nutrient-rich foods include:
- Spinach
- Kale
- Broccoli
These foods are nutrient-rich because they have a high number of vitamins and minerals.
All three of these are easy to find in grocery stores. The only thing you need to do is cook them, and they can be eaten as a side dish or mixed into other dishes for more flavor!
Conclusion
You need to eat a wide variety of nutrients for the body to function properly. Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all essential, but it is also vital that you include other vitamins and minerals from fruits and vegetables into your diet as well. Consider adding more seafood, nuts, or leafy greens like spinach to your weekly grocery list!
The common foods listed above have high amounts of nutrients such as vitamin C, which help support healthy skin, while broccoli has been known to decrease risks for certain types of cancers due to its phytochemicals. There’s no reason not to add these nutrient-rich options with low calories count to your daily meal plans!






